Perkin condensation
Perkin condensation
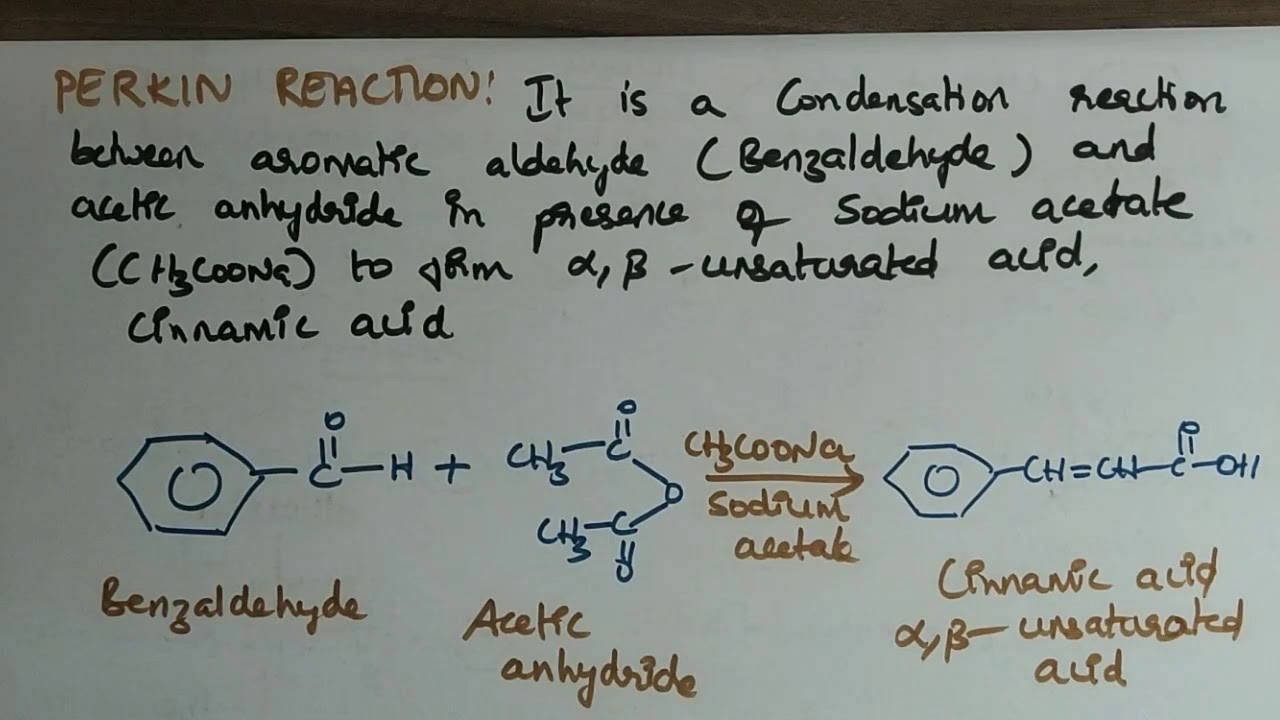
It is type of condensation reaction, which involves the condensation of acidic anhydride (as acetic anhydride) and aromatic aldehyde (benzaldehyde) in the presence of weak base to give unsaturated carboxylic acid. The bases most commonly used are sodium and potassium salt of the acid, potassium carbonate or trimethylamine. In 1968 Perkin described the very first example of such type condensation reaction, involve the synthesis of coumarin by condensing the sodium or potassium salt of salicylaldehyde with acetic anhydride .
Generally, such type of reaction is only applicable to aromatic aldehyde and useful for the preparation of substituted cinnamic acid.
Course Material
- Kinetic control vs thermodynamic control
- Selectivity (stereo, regio, chemo)
- Active methylene compounds
- Aldol Condensation
- Claisen condensation
- Cross Claisen Condensation
- Reformatsky Reaction
- Stobbes Condensation
- Darzen condensation
- Perkin condensation
- Wittig Reaction
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
- SN Reactions I
- SN Reactions II
- SN Reactions III
- Nucleophilic Substitution Prime Reactions
- Neighbouring group participation
- Aromatic Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
- NAS Elimination Addition
- NAS Addition Elimination
- Aromatic Nucleophilic Reactions (diazonium salts)
- Elimination Reactions
- Reactive intermediates
- Chapters 23
- Department Chemistry
- Teacher
Dr. Syed Gohar Taqi Kazimi


