Cross Claisen Condensation
Mixed Claisen Condensation
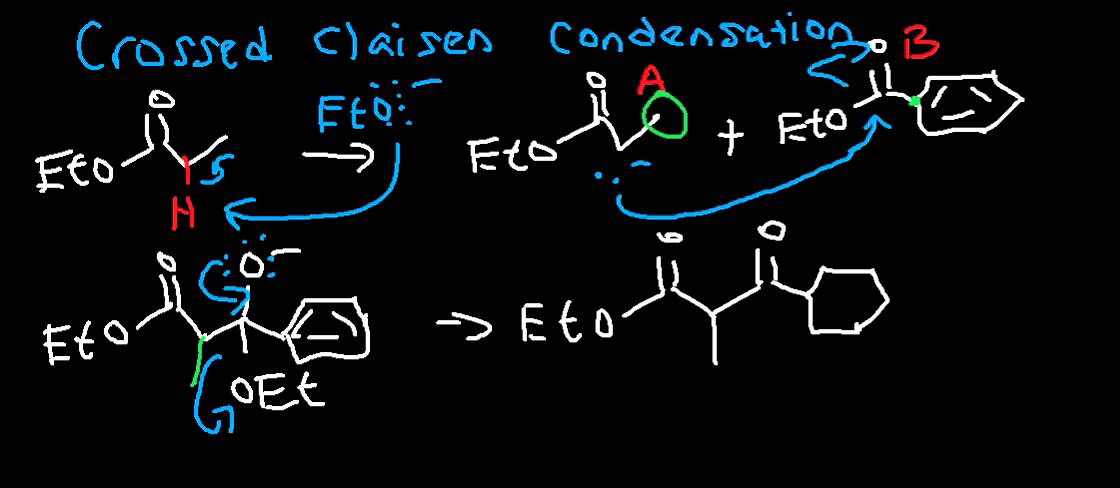
A mixed Claisen condensation (Crossed Claisen condensation) is a condensation reaction between two different esters. Like a mixed Aldol reaction, a mixed Claisen condensation is useful reaction only if it is carried out under those conditions which give rise to only one product. Otherwise the result is the mixture of products which are difficult to separate. In this reaction an ester or ketone with α-hydrogen (ability to form enolate) is condensed with an ester that cannot form an enolate in the presence of a strong base.
For example, reaction of ethylacetate (an ester which can form an enolate and ethyl benzoate (an ester which cannot form an enolate) with sodium methoxide (a strong base) followed by aqueous acid forms Ethyl-3-oxo-3-phenylpropanoate.
A retro-Claisen condensation is the reverse of a Claisen condensation. In this reaction a β-keto ester (or its enol tautomer) is reacted with an excess of strong base, causing fragmentation, and producing two ester products. The β-keto ester must be nonenolizable (lack a proton on the carbon between the two carbonyl groups), otherwise an enolate is formed and no fragmentation occurs.


