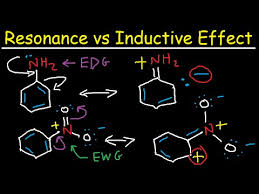
Resonance Effect
Resonance Effect
It is the polarity induced in a pi Bond and lone pair of electron or between two pi bonds.
•Resonance effect is defined as decrease in electron density at and position followed by the increase in electron density at another position.
•The effect may be positive or negative.
•Figure shows the different resonance Structure of different compounds.
Resonance effect may be positive or negative.
Positive resonance effect:
Atoms which donate Electrons toward carbonshow +M effect.
Electron donating groups:
For example- -OH, -SH, -OR,-SR.
Negative resonance effect:
Atoms which accept electrons or withdraw electrons from other atoms show negative resonance effect.
For example- -NO2, C=O, -COOH, -C≡N.
•
Course Material
- Resonance
- Resonance Effect
- Dipole Moment
- Iductive effect
- Hydrogen Bonding
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
- Alkenes and Alkynes
- Wittig Reaction
- Isomerism
- Isomerism I
- optical isomerism
- Aromatic Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions I
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions II
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions III
- Alcohols 1
- Alcohols 2
- Carboxylic Acid 1
- Carboxylic Acid 2
- Aldehyde and ketone
- Base catalyzed reactions of carbonyl compounds I
- Base catalyzed reactions of carbonyl compounds II
- Aldol Condensation
- Reactions of alkyl amines, Arene diazonium salts
- Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
- Chapters 26
- Department Biotechnology
- Teacher
Dr. Syed Gohar Taqi Kazimi


