Aldol Condensation
Aldol Condensation
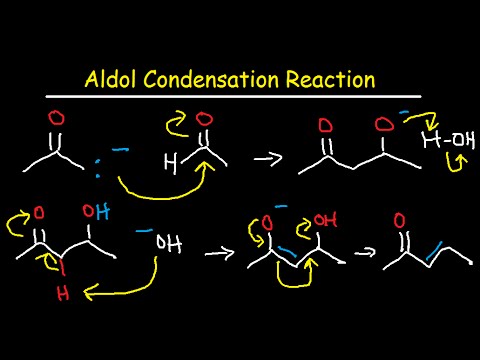
We know that both aldehyde and ketones are electrophiles and therefore can react with nucleophiles. We also know that when a proton is removed from α-carbon of an aldehyde or ketone, the resulting anion is a nucleophile and can react with electrophile. In Aldol Addition both of these activities are present. One molecule of carbonyl compound after removal of proton from α-carbon, reacts as nucleophile and attacks the electophilic carbon of other carbonyl compound.
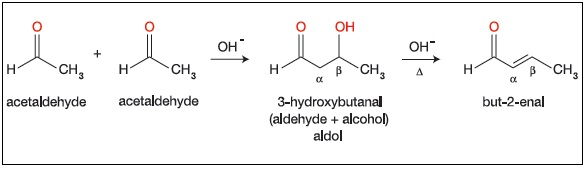
“Two molecules of carbonyl compounds having α-hydrogen condense with each other In the presence of a base to form a product having both aldehyde/ ketone and alcoholic functional groups. This is called Aldol addition.” When the reactant is aldehyde the product is β-hydroxy aldehyde, that’s why thereaction is called an Aldol addition (Ald for aldehyde and ol for alcohol). When the reactant is ketone, the addition product is a β-hydroxy ketone. This is a reversible reaction and good yield is only possible if we remove the product from the solution as it is formed.
If the product of Aldol addition is dehydrated, the overall reaction is called an Aldol condensation. A condensation reaction is a reaction that combines two molecules along with the removal of small molecule like water or an alcohol. β-hydroxy aldehyde and β-hydroxy ketone can also be dehydrated under basic conditions. so heating the aldol addition product in either acid or base results in dehydration. The product would be either α-β-unsaturated aldehyde or ketone.