Week 2: Classification Of Manufacturing Processes
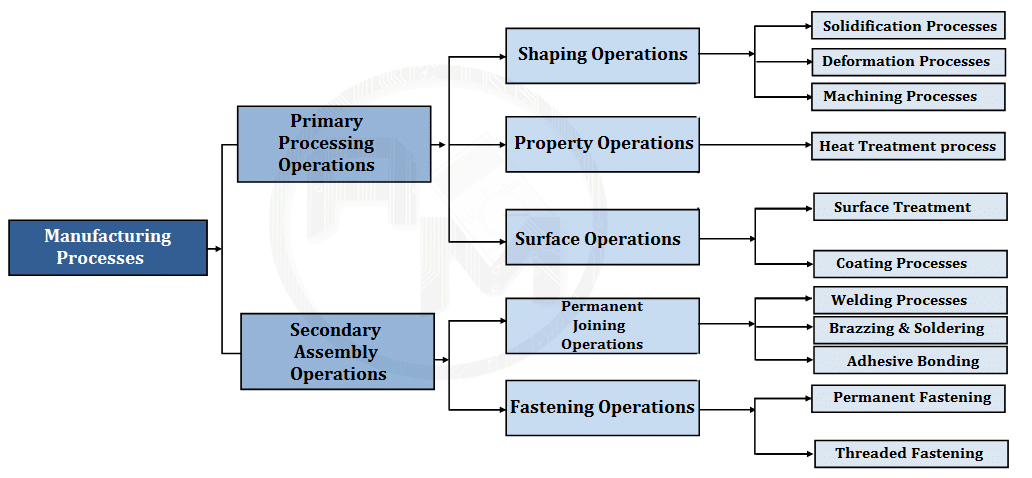
Primary Shaping Processes
Primary shaping processes are manufacturing of a product from an amorphous material. Some processes produces finish products or articles into its usual form whereas others do not, and require further working to finish component to the desired shape and size. Castings need re-melting of scrap and defective ingots in cupola or in some other melting furnace and then pouring of the molten metal into sand or metallic moulds to obtain the castings. Thus the intricate shapes can be manufactured. Typical examples of the products that are produced by casting process are machine beds, automobile engines, carburetors, flywheels etc. The parts produced through these processes may or may not require to under go further operations. Some of the important primary shaping processes is:
(1) Casting, (2) Powder metallurgy, (3) Plastic technology, (4) Gas cutting, (5) Bending and
(6) Forging
Secondary or Machining Processes
As large number of components require further processing after the primary processes. These components are subjected to one or more number of machining operations in machine shops, to obtain the desired shape and dimensional accuracy on flat and cylindrical jobs. Thus, the jobs undergoing these operations are the roughly finished products received through primary shaping processes. The process of removing the undesired or unwanted material from the workpiece or job or component to produce a required shape using a cutting tool is known as machining. This can be done by a manual process or by using a machine called machine tool (traditional machines namely lathe, milling machine, drilling, shaper, planner, slotter). In many cases these operations are performed on rods, bars and flat surfaces in machine shops. These secondary processes are mainly required for achieving dimensional accuracy and a very high degree of surface finish. The secondary processes require the use of one or more machine tools, various single or multi-point cutting tools (cutters), job holding devices, marking and measuring instruments, testing devices and gauges etc. for getting desired dimensional control and required degree of surface finish on the workpieces. The example of parts produced by machining processes includes hand tools machine tools instruments, automobile parts, nuts, bolts and gears etc. Lot of material is wasted as scrap in the secondary or machining process. Some of the common secondary or machining processes are— (1) Turning, (2) Threading, (3) Knurling, (4) Milling, (5) Drilling, (6) Boring, (7) Planning, (8) Shaping, (9) Slotting, (10) Sawing, (11) Broaching, (12) Hobbing, (13) Grinding, (14) Gear cutting, (15) Thread cutting and (16) Unconventional machining processes namely machining with Numerical Control (NC) machines tools or Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines tools using ECM, LBM, AJM, USM setups etc.


