Week 14: Joining Processes (Soldering and Brazing)
Book Chapter 17 Page 354
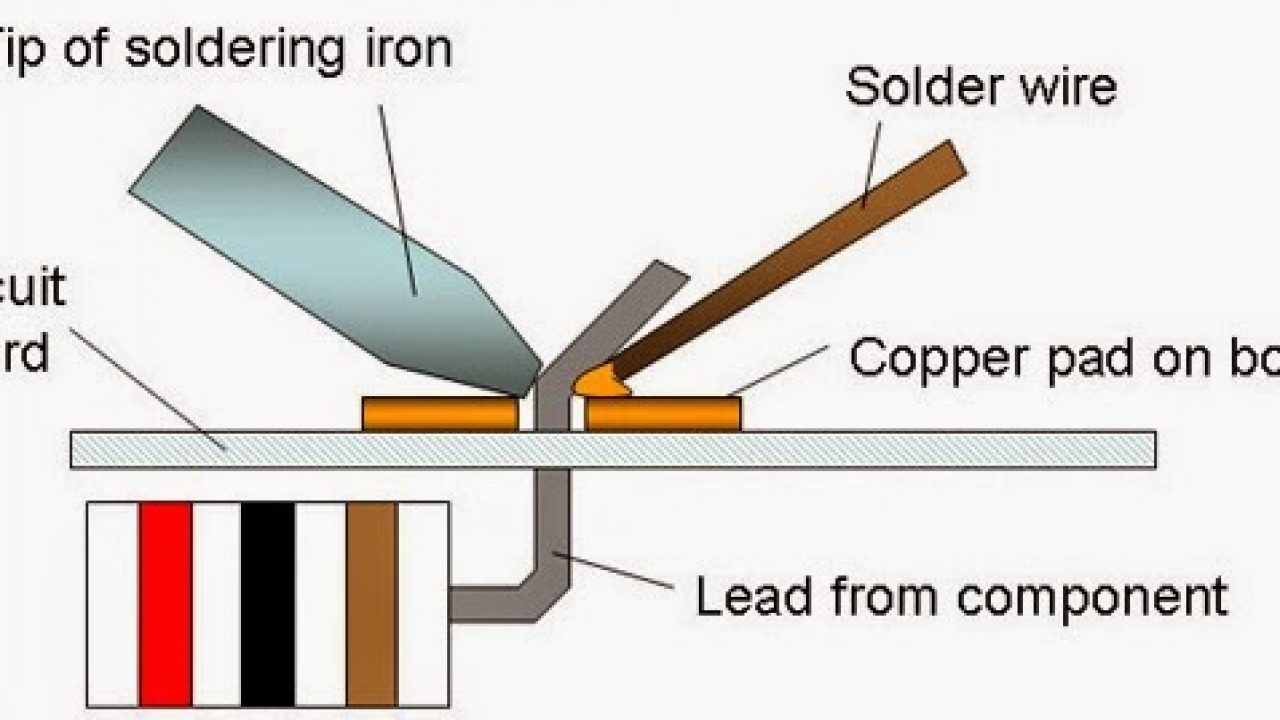
Soldering
Soldering is a method of joining similar or dissimilar metals by heating them to a suitable temperature and by means of a filler metal, called solder, having liquidus temperuatre not exceeding 450°C and below the solidus of the base material. Though soldering obtains a good joint between the two plates, the strength of the joint is limited by the strength of the filler metal used. Solders are essentially alloys of lead and tin. To improve the mechanical properties and temperature resistance, solders are added to other alloying elements such as zinc, cadmium and silver in various proportions. Soldering is normally used for obtaining a neat leak proof joint or a low resistance electrical joint.
Brazing
Like soldering, brazing is a process of joining metals without melting the base metal. Filler material used for brazing has liquidus temperature above 450°C and below the solidus temperature of the base metal. The filler metal is drawn into the joint by means of capillary action (entering of fluid into tightly fitted surfaces). Brazing is a much widely used joining process in various industries because of its many advantages. Due to the higher melting point of the filler material, the joint strength is more than in soldering. Almost all metals can be joined by brazing except aluminum and magnesium which cannot easily be joined by brazing. Dissimilar metals, such as stainless steel to cast iron can be joined by brazing. Because of the lower temperatures used there is less distortion in brazed joints. Also, in many cases the original heat treatment of the plates being joined is not affected by the brazing heat. The joint can be quickly finished without much skill. Because of the simplicity of the process it is often an economical joining method with reasonable joint strength. The brazed joints are reasonably stronger, depending on the strength of the filler metal used. But the brazed joint is generally not useful for high temperature service because of the low melting temperature of the filler metal. The color of the filler metal in the brazed joint also, may not match with that of the base metal. Because the filler metal reaches the joint by capillary action, it is essential that the joint is designed properly. The clearance between the two parts to be joined should be critically controlled. Another important factor to be considered is the temperature at which the filler metal is entering the join


