Week 2: Kinetic Theory of Gases. Derivation of Fundamental Equation of Kinetic Theory of Gases.
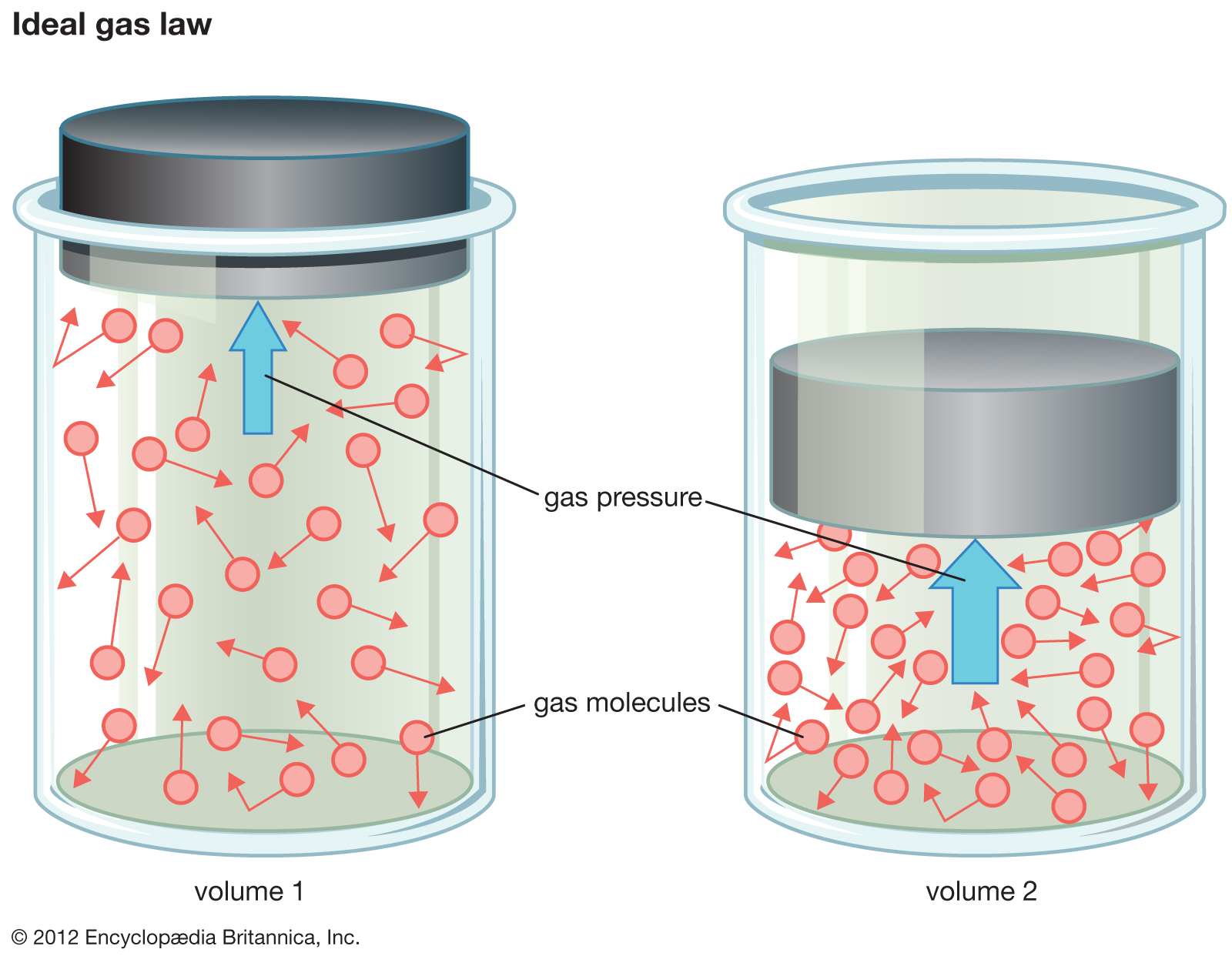
The British scientist James Clerk Maxwell and the Austrian physicist Ludwig Boltzmann, in the 19th century, led in establishing the theory, which became one of the most important concepts in modern science. The simplest kinetic model is based on the assumptions that the gas is composed of a large number of identical molecules moving in random directions, separated by distances that are large compared with their size; the molecules undergo perfectly elastic collisions (no energy loss) with each other and with the walls of the container, but otherwise do not interact; and the transfer of kinetic energy between molecules is heat. These simplifying assumptions bring the characteristics of gases within the range of mathematical treatment.


