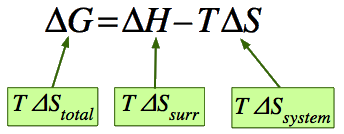
Week 14: Helmholtz Energy and Gibbs Energy, The Maxwell Relationship
Gibbs free energy (G) is a measure of the maximum available work that can be derived from any system under conditions of constant temperature (T) and pressure (P). G is a thermodynamic “state function”, i.e., an equilibrium property that depends only upon the conditions—such as T, P and electrical, magnetic and gravitational fields—imposed on the system being considered, and not on that system’s past history. Since absolute G values cannot be determined, changes in G as a system goes from one state to another become the main focus of attention. These ΔG (“delta-G”) values are highly informative. if ΔG (= G final state − G initial state) is negative, the process observed liberates energy: it will occur spontaneously and can be harnessed to do useful work. For chemical changes, tabulated standard free energy values can be used to predict the direction and energy yield of a particular reaction.


