Week 4: Cellular Metabolism
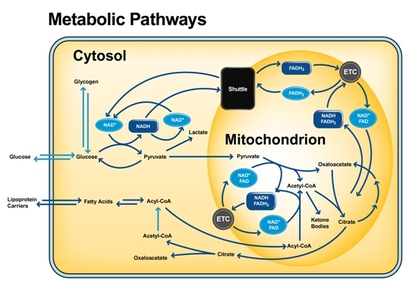
Cellular metabolism can break down organic matter, a process known as catabolism. Cellular metabolism can also produce substances, a process referred to as anabolism. To provide a more graspable example, breaking down food so the nutrients can be utilized is a catabolic reaction. The production of proteins from amino acids is an example of an anabolic reaction.In general, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy. Amino acids, carbohydrates, and lipids are vital for life. Metabolic reactions either produce these molecules during the construction of cells and tissue or digest them and use them as a source of energy. Cellular metabolism is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Reference:
- Master Success Text Book of Botany D by Dr. Riaz-ul-Ramay
- Cell Biology; Cytology, Biomolecules and Molecular Biology by PS VERMA, V K AGRWAL and S CHAND


