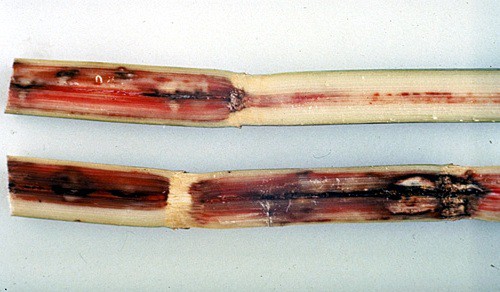
Red Rot of Sugarcane:
Description:
- One of the oldest & widely distributed in Punjab & Sindh
History and Importance:
- First reported from Java in 1883
- In sub-continent in 1906
Etiology:
Causal organism: Colletotrichum falcatum
Order: Melanconiales
Family: Melanconiaceae
Symptoms:
- Yellowing and dropping of 3rd or 4th leaf from the top
- Midrib of leaves is also affected producing red patches with ash colored center having abundant fungal growth.
- Infected canes are lighter in weight and are easily broken.
- If split open longitudinally especially when withering of leaves starts, pith is found reddened.
Disease cycle:
- Fungus survive in soil & on planting material
- Ratoon*( cutting most of the above-ground portion but leaving the roots and the growing shoot apices*(growing points) intact so as to allow the plants to recover and produce a fresh crop in the next season) crop may also help in disease development
- Rain, irrigation water, wind & insects also spread the disease
Epidemiology:
- 27-30°C & High RH
- Humid and warm weather, water logged conditions, lack of proper cultural operations resulting in weeds, continuous cultivation of same variety in a particular locality and presence of susceptible varieties in the vicinity are the main factors determining the epidemic development of the disease.
Management:
- Crop rotation for two years
- Seed setts should be free from disease or treated with solution of Benelat for 1 hr
- Residues should be burn after harvest
- Ratoon crop discouraged if first crop infected
- Resistant thick canes varieties, particularly e.g. CP-77-400, SPF-24O, 237, CPF 72-2O86 etc.
- Treat sets with Formaline solution (1:20), or Benomyl, for10-15 minutes and cover them with wet gunny bags for 3 hours.


