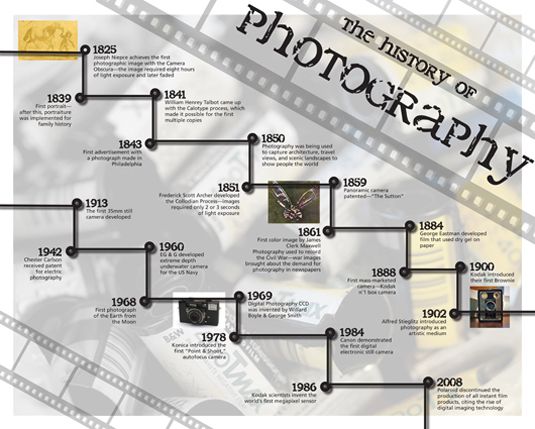
Week 1: Pinholes to Pixels-Historical Perspective
Camera obscura (plural camerae obscurae or camera obscuras, from Latin camera obscūra, “dark chamber”), also referred to as pinhole image, is the natural optical phenomenon that occurs when an image of a scene at the other side of a screen (or, for instance, a wall) is projected through a small hole in that screen as a reversed and inverted image (left to right and upside down) on a surface opposite to the opening. The surroundings of the projected image have to be relatively dark for the image to be clear, so many historical camera obscura experiments were performed in dark rooms. The term "camera obscura" also refers to constructions or devices that make use of the principle within a box, tent, or room. Camera obscuras with a lens in the opening have been used since the second half of the 16th century and became popular as an aid for drawing and painting. The camera obscura box was developed further into the photographic camera in the first half of the 19th century when camera obscura boxes were used to expose light-sensitive materials to the projected image.


