Week 10 | Classification of Human Rights
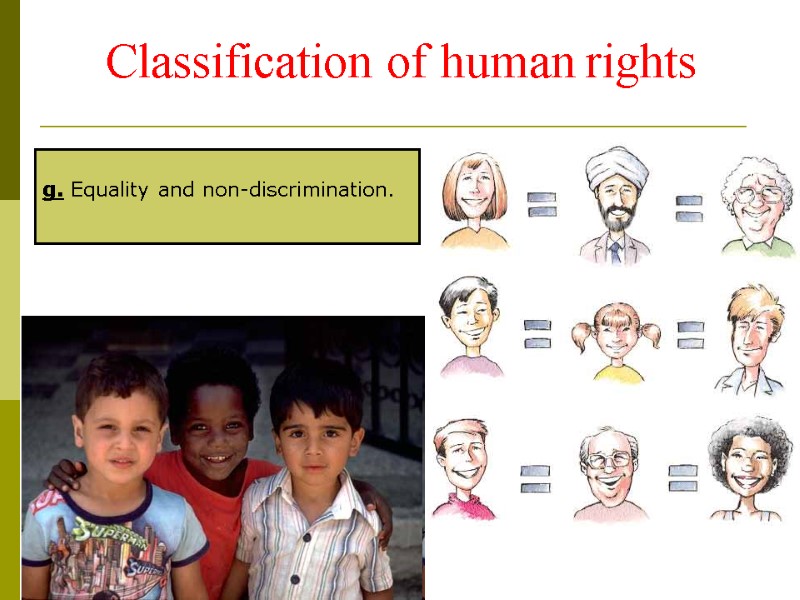
Human rights are commonly understood as being those rights which are inherent in the mere fact of being human. The concept of human rights is based on the belief that every human being is entitled to enjoy her/his rights without discrimination. Human rights differ from other rights in two respects. Firstly, they are characterized by being:
- Inherent in all human beings by virtue of their humanity alone (they do not have, to be purchased or to be granted);
- Inalienable (within qualified legal boundaries); and
- Equally applicable to all.
Secondly, the main duties deriving from human rights fall on states and their authorities or agents, not on individuals.


